Breast cancer has always been one of the most dangerous diseases that threaten women’s lives. If the disease is not detected in the early stages, it can result in the death of the patient. The term breast cancer is referring to a malignant tumor that happened due to the unexpected development of breast’s cells which can probably have the ability to spread through other different parts of the patient’s body. The occurrence of cancer is often a result of the abnormal growth of cells in our bodies. Cancers generally are classified into two types, Benign (non-cancerous cell) and Malignant (cancerous cell). The earlier the cancer is diagnosed, the better the patient’s chance of recovery. Being able to accurately predict breast cancer present in patients has always been an important issue for cancer researchers.
The study focuses on distinguishing between benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) cells in breast cancer diagnosis. By applying multiple classification algorithms alongside various feature selection strategies, the research seeks to determine the most accurate methods for early detection.
Multiple classifiers—including decision trees, support vector machines, and k-nearest neighbors—were rigorously tested. Each model was fine-tuned and evaluated based on performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, and recall. The findings reveal that an optimal combination of feature selection strategy and classification algorithm can significantly enhance predictive performance, offering a robust tool for early diagnosis.
This project’s innovative methodology and impactful results were recognized on an international stage, winning 1st Prize for the Best Paper Award at the 5th International Conference on Informatics and Computational Sciences (ICICoS 2021) held at Diponegoro University in Indonesia.
Methodology
The proposed methodology follows a structured approach, using machine learning algorithms to classify breast cancer data and evaluate their performance.
Data Collection & Preprocessing
- The Breast Cancer Wisconsin (Diagnostic) dataset from the UCI Machine Learning Repository was used.
- The dataset contains various features, including radius, texture, smoothness, and symmetry, of cell nuclei present in breast cancer biopsies.
- Preprocessing steps involved handling missing values, scaling the features, and normalizing the data to ensure consistent and effective model training.
Feature Selection
Two feature selection techniques were used:
- Correlation-based feature selection: This approach identified the most important features based on their correlation with the target variable (cancer diagnosis).
- Recursive Feature Elimination (RFE): This method, applied with the Random Forest classifier, was used to select the best features for better model performance.
Machine Learning Models
The following machine learning classifiers were used:
- Support Vector Machine (SVM): Chosen for its ability to work well with high-dimensional datasets.
- Random Forest: A versatile classifier known for its robustness in handling various datasets.
- K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN): Used for its simplicity and effectiveness in classification tasks.
- Naive Bayes: A probabilistic classifier used to estimate the likelihood of outcomes based on input data.
Model Evaluation
Confusion matrix was used to evaluate model performance, with metrics including:
- Accuracy
- Precision
- Recall
- F1-Score
- The performance of each model was compared based on these metrics after applying the feature selection techniques.
Results & Key Findings
The experiment demonstrated the following results:
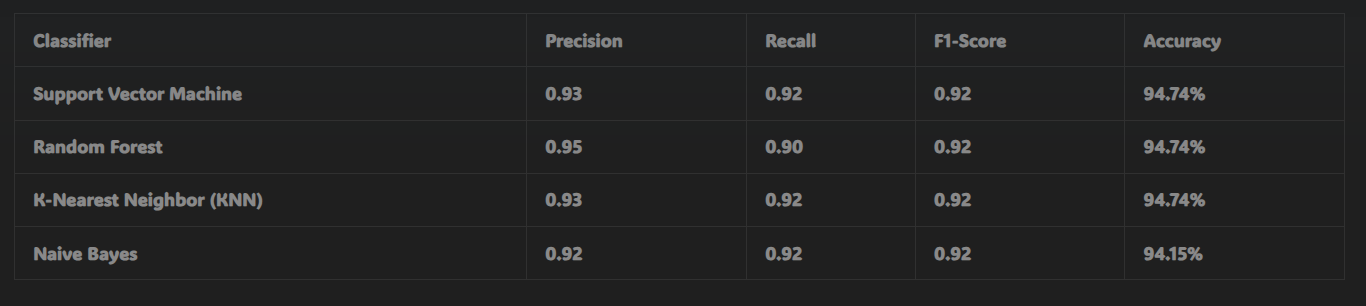
- After applying correlation-based feature selection, the best accuracy achieved was 94.74% for the SVM, Random Forest, and KNN classifiers.
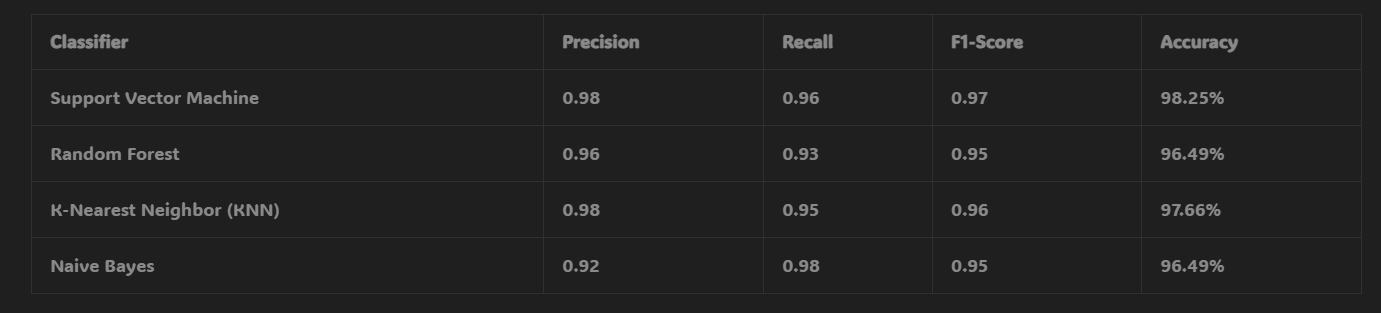
- With RFE-based feature selection, the accuracy improved significantly, with the SVM achieving the highest accuracy of 98.25%.
- The Random Forest and KNN models showed accuracy rates of 96.49% and 97.66%, respectively, with Naive Bayes achieving 96.49%.
These results highlight the importance of feature selection techniques, as the RFE-based method significantly improved the model’s ability to predict breast cancer accurately.
Confusion Matrix Results with RFE-Based Feature Selection
CONCLUSION
Significance & Contributions
✅ Feature Selection Impact: Demonstrated how different feature selection methods (correlation-based and RFE) impact the accuracy of classification models for breast cancer prediction.
✅ Model Performance: Showcased the effectiveness of machine learning algorithms (SVM, Random Forest, KNN, and Naive Bayes) in predicting breast cancer outcomes with high accuracy.
✅ Potential Healthcare Applications: This research has the potential to be applied in healthcare systems to assist in early cancer detection, improving diagnosis accuracy and helping medical professionals make better decisions.
📄 Full Thesis: View Here
For a comprehensive explanation of the methodology, statistical analysis, and detailed results, please refer to the full research paper on IEEE Xplore:










