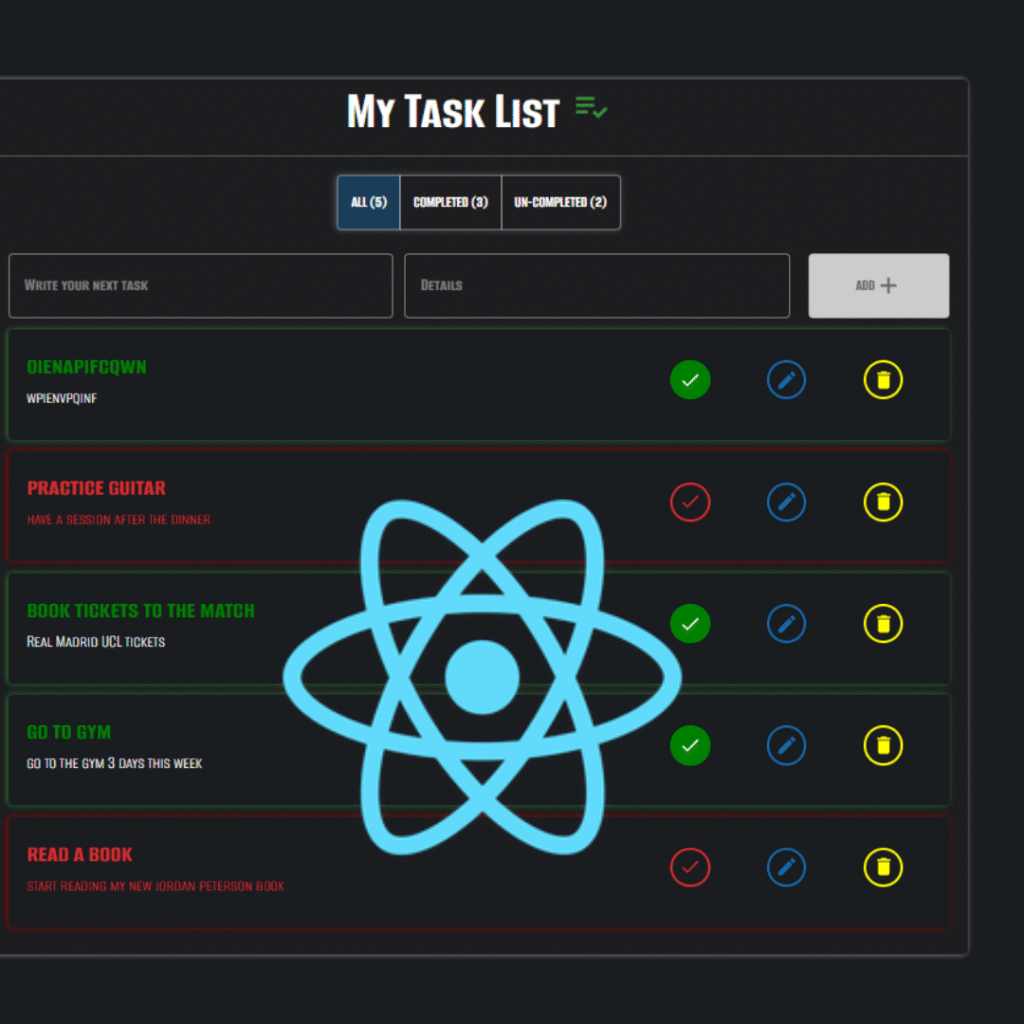
Overview
Code Nest is a comprehensive, full-stack blogging platform designed to emulate a real-world production application. Built with the MERN stack, it provides a seamless experience for both readers and content administrators. The platform includes everything from user authentication and role-based permissions to a powerful admin dashboard, dynamic content management, and a modern, responsive UI. This project was an intensive deep dive into full-stack development, focusing on creating a secure, scalable, and user-friendly application.
Features
User & Authentication
- Secure user registration and login using JWT tokens.
- Social login integration via Google OAuth for a frictionless user experience.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) distinguishing between Admin and regular users.
Content Management (CRUD)
- Full CRUD functionality for blog posts, with a rich text editor (TinyMCE) for an intuitive writing experience.
- Dynamic, admin-defined categories. A single post can belong to multiple categories.
- Image uploads handled seamlessly through Cloudinary for optimized storage and delivery.
API & Data Handling.
Advanced API with Querying, Pagination & Analytics
- Built a powerful, single API endpoint that handles fetching posts with multiple filters: by user, category, search term, and slug.
- Implemented efficient server-side pagination using
skip()andlimit()to ensure fast loading times and scalability, even with a large number of posts. - The endpoint returns rich analytics for the admin dashboard (
totalPosts,lastMonthPosts) directly within the same query, optimizing data fetching.
User Interaction & Discovery
- Users can add, edit, and delete their own comments.
- A dedicated search page with filters to find posts by keywords, publication date (latest/oldest), and specific categories.
Admin Dashboard
- A centralized dashboard for administrators featuring statistics on users, posts, comments, and categories.
- Full moderation capabilities: admins can manage all users, posts, comments, and categories from a single interface.
User Experience (UX)
- System-Wide Dark/Light Theme: A persistent theme toggle allows users to choose their preferred viewing experience, which is saved and maintained across sessions.
- Fully responsive design that provides an optimal experience on desktop, tablet, and mobile devices.
Additional Production Features
- A functional contact form integrated with Brevo (Sendinblue) to send confirmation emails to users and notification emails to the admin.
- Comprehensive schema validation and error-handling middleware on the backend for data integrity and robust API responses.
- Responsive, clean UI built with Tailwind CSS and Flowbite components.
Tech Stack
- Frontend: React, Redux (for state management), Tailwind CSS, Flowbite
- Backend: Node.js, Express.js
- Database: MongoDB with Mongoose ODM
- Authentication: JWT, Google OAuth 2.0
- Rich Text Editor: TinyMCE
- File Storage: Cloudinary
- Email Service: Brevo (Sendinblue) API
- Deployment: Render (Frontend & Backend)
Database Architecture
The MongoDB schema was intentionally designed for scalability and clear data relationships, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
- Users Collection: The central entity storing credentials, profile info, and role.
- Posts Collection: Each post document contains a reference (
author) to theUserwho created it and an array of references (categories) to the Categories collection, establishing a Many-to-Many relationship. - Categories Collection: Admin-defined list of categories. The array of post references within each category allows for flexible querying from both sides of the relationship.
- Comments Collection: Each comment contains a reference to its parent
Postand theUserwho wrote it. The user’s name is embedded within the comment for efficient data retrieval without additional database lookups when rendering the UI. - Efficient Data Querying:
A significant challenge was designing theGET /api/postsendpoint to be flexible enough for the homepage, search page, and admin dashboard without being inefficient. I leveraged MongoDB’s query operators and theskip()&limit()methods to create a single, powerful endpoint that handles filtering, sorting, pagination, and even returns aggregate analytics data like the count of posts from the last month. This keeps the frontend code simple and the backend performant.
This structure ensures data integrity while optimizing for the most common query patterns, like fetching all posts with their author’s name and categories.
Challenges & Learnings
- Focused State Management: A key decision was to use Redux not for all state, but for global state that truly needed it. I managed the user’s authentication state and the theme preference globally, while using local component state for UI-specific interactions. This taught me to choose the right tool for the job, avoiding unnecessary boilerplate while keeping state predictable and accessible where it mattered most.
- Secure Authentication Flow: Implementing both JWT and OAuth required a deep understanding of secure backend practices. I learned to properly manage tokens, secure routes with middleware, and handle sensitive user data responsibly.
- Database Schema Design: Designing the Many-to-Many relationship between Posts and Categories was a key learning experience. It taught me to model data based on how it would be accessed, prioritizing performance for common use cases.
- Persistence of User Preference: Implementing the dark/light theme to persist across browser sessions involved combining Redux state with local storage, providing a seamless user experience.
- Deployment & Environment Variables: Deploying a full-stack app with connected services on Render taught me the critical importance of properly configuring environment variables and ensuring the build process works correctly in a production environment.
- Designing a Scalable Data API
- The initial approach of creating separate endpoints for each use case (homepage, search, user posts) would have led to messy and inefficient code. The challenge was to design a single, maintainable solution that was both flexible and performant.
- Learning & Solution: I leveraged MongoDB’s powerful query operators and the flexibility of Express.js to build a dynamic
GET /api/postscontroller. It intelligently constructs database queries based on URL parameters, handling pagination, filtering, and search in one place. This taught me the importance of abstracting complexity on the server to keep the frontend simple and the entire application more scalable and easier to maintain.
- Learning & Solution: I leveraged MongoDB’s powerful query operators and the flexibility of Express.js to build a dynamic
Future Improvements
To further enhance the application’s security, engagement, and robustness, the following features are planned:
- Enhanced Security: Implementing rate limiting on authentication routes to protect against brute-force attacks.
- User Engagement: Adding a post likes/favorites system to increase user interaction and content discoverability.
- Performance Optimization: Integrating Redis to cache frequent database queries, significantly improving response times for popular content.
- Code Reliability: Developing a comprehensive suite of unit and integration tests to ensure feature stability and prevent regressions.
See It In Action
The best way to experience Code Nest is to use it yourself! Explore the public blog, test the search functionality, and see the full user flow.
- 🌐 Live Demo: https://mhd-mern-blog.onrender.com
- 👤 Admin Demo Access:
- Email:
admin@hotmail.com - Password:
admin123
- Email:
- 💻 Explore the Codebase: Github